Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (16): 3002-3009.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.16.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Antimicrobial composite resin: Antibacterial ability
Che Xiao-qiang, Zhang Song-ying, Chen Yun-ping, Liu Bin
- Stomatology School, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2012-08-15Revised:2012-09-26Online:2013-04-16Published:2013-04-16 -
Contact:Liu Bin, Doctor, Professor, Stomatology School, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China liubkq@lzu.edu.cn -
About author:Che Xiao-qiang★, Studying for master’s degree, Lecturer, Stomatology School, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China 526732521@qq.com -
Supported by:the Scientific Supporting Plan of Gansu Province, No. 1204FKCA180*; the Scientific and Technological Plan of Gansu Province, No. 1107RJYA002*; the Scientific and Technological Research Fund of Lanzhou University Stomatology School, No. 2011-07*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Che Xiao-qiang, Zhang Song-ying, Chen Yun-ping, Liu Bin. Antimicrobial composite resin: Antibacterial ability[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(16): 3002-3009.
share this article
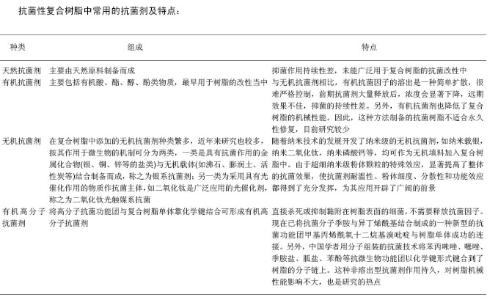
2.1 抗菌性复合树脂的定义及要求 抗菌性复合树脂是指在复合树脂中添加抗菌剂,使其本身具有抗菌性,在一定时间内将黏在上面的细菌杀死或抑制其增殖。一般要求抗菌性复合树脂制品的抗菌性具有高效、广谱、持续性好、无毒无异味、具有良好的生物相容性和机械性能[7]。 2.2.1 天然抗菌剂 主要由天然原料制备而成,但种类不多,且抑菌作用持续性差,未能广泛用于复合树脂的抗菌改性中。如壳聚糖,具有很好的抗菌作用,但在复合树脂中应用不多。 2.2.2 有机抗菌剂 主要包括有机酸、酯、醇、酚类物质,最早用于树脂的改性当中。如洗必泰,抗生素等,与无机抗菌剂相比,有机抗菌因子的溶出是一种简单扩散,很难严格控制,前期抗菌剂大量释放后,浓度会显著下降,远期效果不佳,抑菌的持续性差。Takemura 等[8]研究表明,将含有醋酸洗必泰的复合树脂浸入水中,5 d后溶出的抗菌因子浓度明显降低。另外,有机抗菌剂也降低了复合树脂的机械性能。因此,这种方法制备的抗菌树脂不适合永久性修复,目前研究较少。 2.2.3 无机抗菌剂 在复合树脂中添加的无机抗菌剂种类繁多,近年来研究也较多,按其作用于微生物的机理可分为两类,一类是具有抗菌作用的金属化合物(银、铜、锌等的盐类)与无机载体(如沸石、膨润土、活性炭等)结合制备而成,称之为银系抗菌剂;另一类为采用具有光催化作用的物质作抗菌主体,如二氧化钛是广泛应用的光催化剂,称之为二氧化钛光触媒系抗菌[9] 。随着纳米技术的发展开发了纳米级的无机抗菌剂,如纳米载银,纳米二氧化钛,纳米磷酸钙等,均可作为无机填料加入复合树脂中。由于超细纳米级粉体颗粒的特殊效应,显著提高了整体的抗菌效果,使抗菌剂耐温性、粉体细度、分散性和功能效应都得到了充分发挥,为其应用开辟了广阔的前景。目前有研究表明金属离子杀灭和抑制细菌的活性按下列顺续递减:Ag+>Hf 2+ >Cd 2+ >Cr 3+ >Ni 2+ >Pb 2+ > Co 4+ >Zn 2+ >Fe 3+ 。因此在无机抗菌剂中对银系抗菌剂研究最多,但它存在易变色的缺点[10] 。 2.2.4 有机高分子抗菌剂 将高分子抗菌功能团与复合树脂单体靠化学键结合可形成有机高分子抗菌剂。直接杀死或抑制黏附在树脂表面的细菌,不需要释放抗菌因子。现在已将抗菌分子季胺与异丁烯酰基结合制成的一种新型的抗菌功能团甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡啶与树脂单体成功的连接。另外,中国学者用分子组装的抗菌技术将苯丙咪唑、噻唑、季胺盐、胍盐、苯酚等抗微生物功能团以化学键形式键合到了树脂的分子链上。这种非溶出型抗菌剂作用持久,对树脂机械性能影响不大,也是研究的热点[11] 。 2.3 抗菌性复合树脂 2.3.1 纳米载银抗菌性复合树脂 Ag+的杀菌能力在很长时间以前已经得到学者们的认可,它对众多口腔病原菌都具有良好的抗菌活性,应用于复合树脂中可发挥良好的抗菌作用,纳米载银抗菌性复合树脂主要依靠释放Ag+起到杀菌的作用,具有抗菌谱广、安全无毒、不产生耐药性等特点。目前对于Ag+抗菌机制尚未完全清楚,一般认为有两种,一是Ag+通过接触反应产生抗菌作用的。它与细菌接触后,与细胞膜结合继而进入细胞,破坏细胞内酶的活性,最后导致细菌死亡。之后它又会游离出菌体重复杀菌过程,因此,抗菌菌能力持久。二是Ag+也具有一定的光催化抗菌能力。在一定波长光照射下,Ag+能催化活性中心,激活水和空气中的氧,产生•OH和活性氧离子(O 2- ),在短时间内破坏细胞的增殖,致使细胞死亡杀死细菌[12] 。 佘文君等[13]比较研究了6种国内外知名品牌纳米级载银无机抗菌剂对口腔病原菌抗菌活性的影响,发现纳米级载银无机抗菌剂对变形链球菌、乳酸杆蔺、黏性放线菌、白色念珠菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠埃希菌均有良好的杀菌效果,且综合抗菌实力相当。Fan等[14]利用不同浓度的苯甲酸银,在复合树脂中成功合成纳米银。纳米银均匀的分布在树脂中,在试管内浸泡4周后,仍释放大量的Ag+。对比研究0.2%和0.5%苯甲酸银的抗菌效果,分别具有52.4% 和 97.5%的抗菌效果。Cheng等[15]利用一种独特的方法制备了纳米银,发现纳米银能均匀分布在复合树脂中,发现质量分数为0.08%时,树脂修复体表面的菌斑减少了40%。另外,纳米载银无机抗菌剂的加入也不会显著影响复合树脂的机械性能。张林祺等[16]比较空白组、0.5%、1.0%、1.5%、2.0%加入纳米载银抗菌剂复合树脂的抗压强度、挠曲强度、耐磨性,各组之间均无显著差异,但以加入1.5%时性能最为理想。 银和银的化合物均具有抗菌性,均可作为抗菌剂。但是,对银及其化合物抗菌性能比较研究发现,银的化合物作为载银抗菌剂,表现为极快的Ag+释放速率和极强的抗菌效果,Ag+释放速率限制了其长期抗菌效果;与之相反,纯银能储备大量的Ag+ ,缓慢释放保证了长期抗菌效果[17-18] 。Kassaee等[17]证明将还原的50n m银颗粒加入到复合树脂中,这些纳米银轻微聚集在一起,具有极稳定的Ag+释放速率,且质量分数为0.5%的载银抗菌剂具有最佳的抗菌效果,而不影响树脂的机械性能。 2.2 抗菌性复合树脂中常用的抗菌剂 抗菌剂分为天然、有机、无机、有机高分子抗菌剂。 目前,纳米载银抗菌性复合树脂还处于研究阶段。体外研究证实银系无机抗菌剂对多种口腔细菌均有杀菌抑菌作用。但对于纳米载银抗菌性复合树脂在口腔复合树脂中的长效性、稳定性、颜色,以及对口腔微生态环境的影响等问题还有待于进一步研究。 2.3.2 季胺盐抗菌性复合树脂 季铵盐的细胞毒性低,具有极高的抗菌性能,被广泛应用于饮水消毒,食品,药品和医疗保健产品中。由于小分子季胺盐因为存在易挥发、化学稳定性差、易产生耐药性、分解产物常带有毒性等缺点,目前研究较少,主要集中于高分子季胺盐的研究。 高分子季铵盐型抗菌单体分子含有带正电的氮原子和长链烷基结构,其抗菌作用基于杀菌还是抑菌还尚未清楚。一方面,细胞壁和细胞膜由磷脂双分子层组成,均带负电荷,从而细菌容易被抗菌材料上的阳离子所吸引,降低细菌的活动能力,抑制其呼吸功能,使其发生“接触死亡”;另一方面,细菌在电场引力的作用下,细胞壁和细胞膜上的负电荷分布不均,细胞膜因不能承受渗透压而变形,发生物理性破裂,使胞内物质如水、蛋白质等泄漏,发生“溶菌”现象而死亡[19] 。 研究开发具有抗菌功能的树脂基牙科材料是口腔科学中一个长期的发展目标,而常用的牙科树脂单体均没有抗菌活性。季铵盐是一种高效广谱的有机抗菌剂,具有低毒、性能稳定、低腐蚀等特点,并表现出长期的生物学效应。将季铵盐型抗菌单体引入于牙科修复材料高分子体系中,赋予牙科材料有效、持久的抗菌性能,必将对龋病及其它继发细菌感染性口腔疾病的防治产生深远影响。祁玲玲[19]实验的主要内容包括:设计、合成了交联和非交联型两类可聚合季铵盐类单体,傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)和核磁共振波谱(1 H-NMR)对产物结构进行了表征。利用在口腔修复医学临床中通用的光固化方法,在树脂基牙科材料中共聚引入季铵盐抗菌单体,制备具有抗菌性能的高分子树脂基牙科修复材料。考察树脂体系中光引发剂、助引发剂等工艺条件对聚合反应的影响,确定了共聚的最佳反应条件。加入交联型抗菌单体的树脂体系双键转化率比非交联单体高17%左右,有利于降低单体的残余,显著提高使用安全性。考察了系列季铵盐单体对常见口腔病菌的最低抑菌浓度(MIC)及最小杀菌浓度(MBC)。选择3种抗菌性较强的单体考察对主要口腔致病菌-变形链球菌的杀菌动力学。利用噻唑蓝比色法(MTT法)测试了MAE-DB和MAE-HB单体的细胞毒性。DMAE-CB、MAE-DB和MAE-HB表现出较强的杀菌性;DMAE-CB在质量浓度19.2 mg/L (4*MBC)与菌液混合培养10 min后,杀菌率可达100%;4*MBC的MAE-DB与变形链球菌接触10 min后没有活菌存在;4*MBC的MAE-HB与变形链球菌接触30 min后没有活菌存在。MAE-DB和MAE-HB对人牙龈成纤维细胞的半数致死浓度为5-10 mg/L,与树脂基质Bis-GMA的细胞毒性相当。 研究了抗菌共聚树脂材料的物理化学特性。修复树脂的硬度随着单体加入量的增加而增大,而加入交联型抗菌单体的树脂硬度更高。所有树脂材料的吸水性均≤40 μg/mm3。使用激光共焦扫描显微镜(CLSM)和扫描电子显微镜(SEM)初步研究了共聚改性树脂的抗菌特性。材料通过破坏变形链球菌生物膜的完整性及抑制生物膜内菌体的活性而发挥接触抗菌活性;并对菌体有直接的破裂作用。 根据烷基长链结构不同,可以形成不同类型的季铵盐抗菌单体。如甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡啶,二甲基丙烯酸季铵盐,正十六烷基-二甲基氯化铵等。He等[20]利用甲基丙烯酸二甲氨基乙酯与不同长链的烷基碘化物反应,合成一系列不同长链烷基含碘的季铵盐,对比研究其抗菌性能发现,聚合季铵盐复合物抗菌性能随着单体烷基链的长度(从戊烷基到十六烷基)增加而增加,随后降低(从十六烷基到十八烷基)。 可聚合季铵盐抗菌单体复合进树脂分子中以后,抗菌作用持久且不影响材料的机械性能。有研究发现,在复合树脂中混入质量分数低于0.4%的甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡啶时,完全不会引起离子的析出,但是由于浓度过低,对菌斑抑制作用很弱。Ebi等[21]将甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡啶含量增至2.83%,发现单体析出量很少,且能很好的抑制菌斑的聚集,但对细菌增殖的抑制作用不明显。Beyth 等[22-23]研究发现,在复合树脂中加入1%纳米季胺盐后,没有影响树脂的挠曲强度,同时对变形链球菌具有很强的抗菌性能,且1个月内没有离子析出,保持了原来的机械性和抗菌性。季胺盐抗菌单体通过抑制表面菌斑聚集,减少修复体周围细菌的总量发挥抑菌作用,而不像溶出性抗菌分子那样渗入到细菌的细胞壁和细胞膜内直接杀灭细菌。因此,其抗菌作用更温和。但缺点是表面蛋白吸附影响抗菌效果,还需进一步研究解决此问题以形成有效的临床产品。 2.3.3 纳米磷酸钙抗菌性复合树脂 磷酸钙是一种与生物具有良好亲和性的生物陶瓷材料,作为人工齿根、人工骨、生物骨水泥等生物材料已得到了广泛的应用。此外在食品添加剂、钙剂和催化剂等领域中它也有广泛的应用。因此它是一种安全性很高的抗菌材料[24] 。现在它已经作为无机填料,添加进复合树脂中。 研究已经表明CaP能超水平释放Ca 2+和PO 4- ,并能维持在一定浓度,在因酸侵蚀的牙齿区域内可以实现再矿化作用,形成羟基磷灰石,恢复矿物质的流失,修复牙体组织缺失[25] 。但是其机械性能低,影响复合树脂的机械性能。近年来,学者们利用喷雾干燥技术制备出了粒度为100 nm的纳米磷酸钙,作为填料加入树脂。这种树脂具有普通CaP复合树脂相同的离子释放度,同时,能达到普通CaP复合树脂2倍的机械强度。在酸性条件下,他能灵敏的释放Ca2+和PO4-,调节pH值,这些离子与抗菌防龋有很大关系[26-27] 。 Moreau等[28]分别添加质量分数为10%,20%,30%,40%的纳米磷酸钙至复合树脂中,与市场上的高强度纤维材料、micro-fill composite、树脂玻璃离子材料比较挠曲强度、中和酸能力、对变形链球菌的抑菌性。结果显示,随着纳米磷酸钙含量的增加,树脂挠曲强度减小,但10%含量的强度(121±10) MPa与高强度纤维材料的强度(120±13) MPa相当,且40%组与micro-fill composite机械强度基本一致,达到了树脂玻璃离子的二三倍;另外40%组能在10 min内使pH值=4的乳酸溶液变化为pH值=5.69,其他材料基本无变化;对变形链球菌的抑菌圈面积达(2.5±0.7) mm2,其他材料没有显示出抑菌圈。因此含纳米磷酸钙的复合树脂具有良好的机械性能,中和酸的能力和抑制链球菌生长的能力,对于减少继发龋的发生和修复体折裂有很好的作用,但临床上的应用还需更深的研究。 2.3.4 新型复合抗菌剂的抗菌性复合树脂 随着对各种有机、无机、高分子抗菌剂的研究,学者们已经初步了解到了他们各自不同的优点,合成了一部分抗菌性复合树脂,并应用到了临床。但是临床上的应用效果并不理想,远未达到抗菌性及机械性能的要求。这就说明含单一抗菌剂的复合树脂不是理想的材料,需要将各种抗菌剂取长补短,制成复合抗菌剂,作为填料加入复合树脂中,从而使复合树脂的抗菌性和机械性达到一个理想的程度。学者们对此也进行了许多研究,希望能研制一种新型的复合抗菌剂。 Cheng等[29]第1次将40%磷酸四钙和不同质量分数(0%,6%,12%,18%)的二甲基丙烯酸季胺盐复合进树脂当中。研究发现二甲基丙烯酸季胺盐的质量分数与磷酸四钙-二甲基丙烯酸季胺盐复合树脂的抗菌性能成线性关系,相关系数为0.98。随着二甲基丙烯酸季胺盐质量分数增加,其抗菌性能增强,当质量分数为18%时,复合树脂的变异链球菌菌落数,新陈代谢活动和产酸量仅为不加二甲基丙烯酸季胺盐的1/2。其领导的研究小组还发现复合树脂中添加纳米磷酸钙-二甲基丙烯酸季胺盐,未降低树脂的机械性能,具有和没有添加抗菌剂的普通复合树脂相当的强度和弹性模量。但是其抗菌效果得到了明显的加强,并且在水中老化180 d后,仍具有很高的抗菌性能,其抗菌持久,钙离子和磷酸根离子释放速率稳定[30] 。另外,第1次将二甲基丙烯酸季胺盐、NAg、纳米磷酸钙聚合在一起,作为填料加入复合树脂中,发现这种含有复合抗菌剂的复合树脂制其抗菌性能要优于含单一抗菌剂的复合树脂(P < 0.05),且机械性能与无抗菌剂的复合树脂也基本一致[31] 。 这种将无机抗菌剂与高分子抗菌剂复合应用与复合树脂抗菌改性的研究在Cheng的研究小组中第1次进行开展。除此之外,他们又将有机抗菌剂洗必泰与纳米磷酸钙和NCaF2复合应用。研究发现含有这种复合抗菌剂的树脂的抗菌性能要远优于对照组,且机械性能优良[32] 。 尽管有机、无机以及高分子抗菌剂等形成的复合抗菌剂成功的进入了复合树脂,具有极好的抗菌效果和机械强度,但其长效性和在临床中的应用仍需进一步研究。"
| [1]Mjör IA,Moorhead JE,Dahl JE.Reasons for replacement of restorations in permanent teeth in general dental practice.Int Dent J.2000;50(6):361-366.[2]Peumans M,Van Meerbeek B,Lambrechts P,et al.The influence of direct composite additions for the correction of tooth form and/or position on periodontal health. A retrospective study. J Periodontol.1998;69(4): 422-427.[3]陈治清.口腔生物材料学[M]. 北京: 化学工艺出版社,2004.[4]Menon T,Kumar C,Dinesh K. Antibacterial activity of glass-ionomer restorative cements and polyacid modified composite resin against cariogenic bacteria. Indian J Med Microbiol.2006;24(2):150-151.[5]Hicks MJ,Parkins FM,Flaitz CM.Kinetic cavity preparation effects on secondary caries formation around resin restorations: a polarized light microscopic in vitro evaluation. ASDC J Dent Child.2001;68(2):115-121.[6]Kawai K,Tsuchitan Y.Effects of resin composite components on glucosyltransferase of cariogenic bacterium.J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51(1): 123-127.[7]周正亚. 抗菌性合成树脂概述[J].塑料加工,2000,29(2):22-24.[8]Takemura K,Sakamoto Y,Staninec M,et al. Antibacterial activity of a Bis-GMA based composite resin and antibacterial effect of chlorhexidine incorporation. Jpn J Conserv Dent. 1983; 26:540-547.[9]张林祺,高勃.载银无机抗菌剂对复合树脂抗菌性能和力学性能的影响[D]. 第四军医大学硕士学位论文,2006.[10]虞振飞,刘吉平.纳米无机抗菌剂的分类与抗菌机理研究[J].中国个体防护装备, 2004,12(3): 10-12.[11]李娜,陈吉华.抗菌性树脂修复材料的研究进展[J].中国美容医学, 2006,15(11): 1318-1320.[12]袁鹏,何宏平.银系无机抗菌剂的研究进展[J].化工矿物与加工, 2002,31(10): 5-9.[13]佘文君,张富强. 6种纳米级载银无机抗菌剂对口腔病原菌的抗菌活性比较[J].上海口腔医学,2003,12(5):356-358.[14]Fan C,Chu L,Ralph Rawls H,et al.Development of an antimicrobial resin-A pilot study. Dent Mater.2011;27(4): 322-328.[15]Cheng YJ,Zeiger DN,Howarter JA,et al.In situ formation of silver nanoparticles in photocrosslinking polymers.J Biomed Mater Res B.2011;97B(1):124-131.[16]张林祺,高勃,唐立辉,等. 纳米载银无机抗菌剂对复合树脂机械性能的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2006,15(1):73-76.[17]Kassaee MZ,Akhavan A,Sheikh N,et al.Antibacterial effects of a new dental acrylic resin containing silver nanoparticles. J Appl Polym Sci.2008;110: 1699-1703.[18]Bürgers R,Eidt A,Frankenberger R,et al.The anti-adherence activity and bactericidal effect of microparticulate silver additives in composite resin materials.Arch Oral Boil.2009;54: 595-601.[19]祁玲玲.新型可聚合季铵盐及其在牙科抗菌高分子材料中的应用研究[D]. 南京理工大学硕士学位论文, 2010.[20]He J,Söderling E,Österblad M,et al.Synthesis of methacrylate monomers with antibacterial effects against S. mutans.Molecules.2011;16(11): 9755-9763.[21]Ebi N,Imazato S,Noiri Y,et al.Inhibitory effects of resin composite conaining bactericide-immobilized filler on plaque accumulation. Dent Mater.2001;17(6): 485-491.[22]Yudovin-Farber I,Beyth N,Weiss EI,et al. Antibacterial effect of composite resins containing quaternary ammonium polyethyleneimine nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res.2010;12(2): 591-603.[23]Beytha N,Yudovin-Farberb I,Bahir R,et al. Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing quaternary ammonium polyethylenimine nanoparticles against Streptococcus mutans. Biomaterials.2006;27(21): 3995-4002.[24]王小健,乔学亮,陈建国,等.无机抗菌剂的研究现状及发展趋势[J].陶瓷学报,2003,24(4): 239-244.[25]Langhorst SE,O’ Donnell JNR,Skrtic D.In vitro remineralization of enamel by polymeric amorphous calcium phosphate composite: Quantitative microradiographic study. Dent Mater.2009;25(7): 884-891.[26]Xu HH,Moreau JL,Sun L,et al.Nanocomposite containing amorphous calcium phosphate nanoparticles for caries inhibition. Dent Mater. 2011;27(8): 762-769.[27]Xu HH,Weir MD,Sun L,et al. Strong Nanocomposites with Ca, PO4, and F Release for Caries Inhibition. J Dent Res.2010; 89(1):19-28.[28]Moreau JL,Sun L,Chow LC.Mechanical and acid neutralizing properties and bacteria inhibition of amorphous calcium phosphate dental nanocomposite. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2011;98B(1): 80-88.[29]Cheng L,Weir MD,Limkangwalmongkol P.Tetracalcium phosphate composite containing quaternary ammonium dimethacrylate with antibacterial properties. J Biomed Mater Res B.2012;100B(3): 726-734.[30]Cheng L,Weir MD,Zhang K,et al.Antibacterial nanocomposite with calcium phosphate and quaternary ammonium.J Dent Res.2012;91(5):460-466.[31]Cheng L,Weir MD,Xu HH,et al.Antibacterial amorphous calcium phosphate nanocomposites with a quaternary ammonium dimethacrylate and silver nanoparticles. Dent Mater. 2012;28(5): 561-572.[32]Cheng L,Weir MD,Xu HH,et al.Antibacterial and physical properties of calcium–phosphate and calcium–fluoride nanocomposites with chlorhexidine. Dent Mater.2012;28(5): 573-583. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [5] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [6] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [7] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [8] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [9] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [10] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [11] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [12] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [13] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

